Search
All search results for "q4 e-tron"
(354)

Audi Q4 e-tron
The Audi Q4 e-tron and Audi Q4 Sportback e-tron are being comprehensively upgraded: with a retuned chassis, increased efficiency, characteristic sound, and more standard equipment. In addition to an optimized drive concept and higher charging power, Audi is expanding the range of functions in both models' driver assistance systems. With an optional adaptive driving assistant, they now support lane changes.
 Audi Q4 e-tron
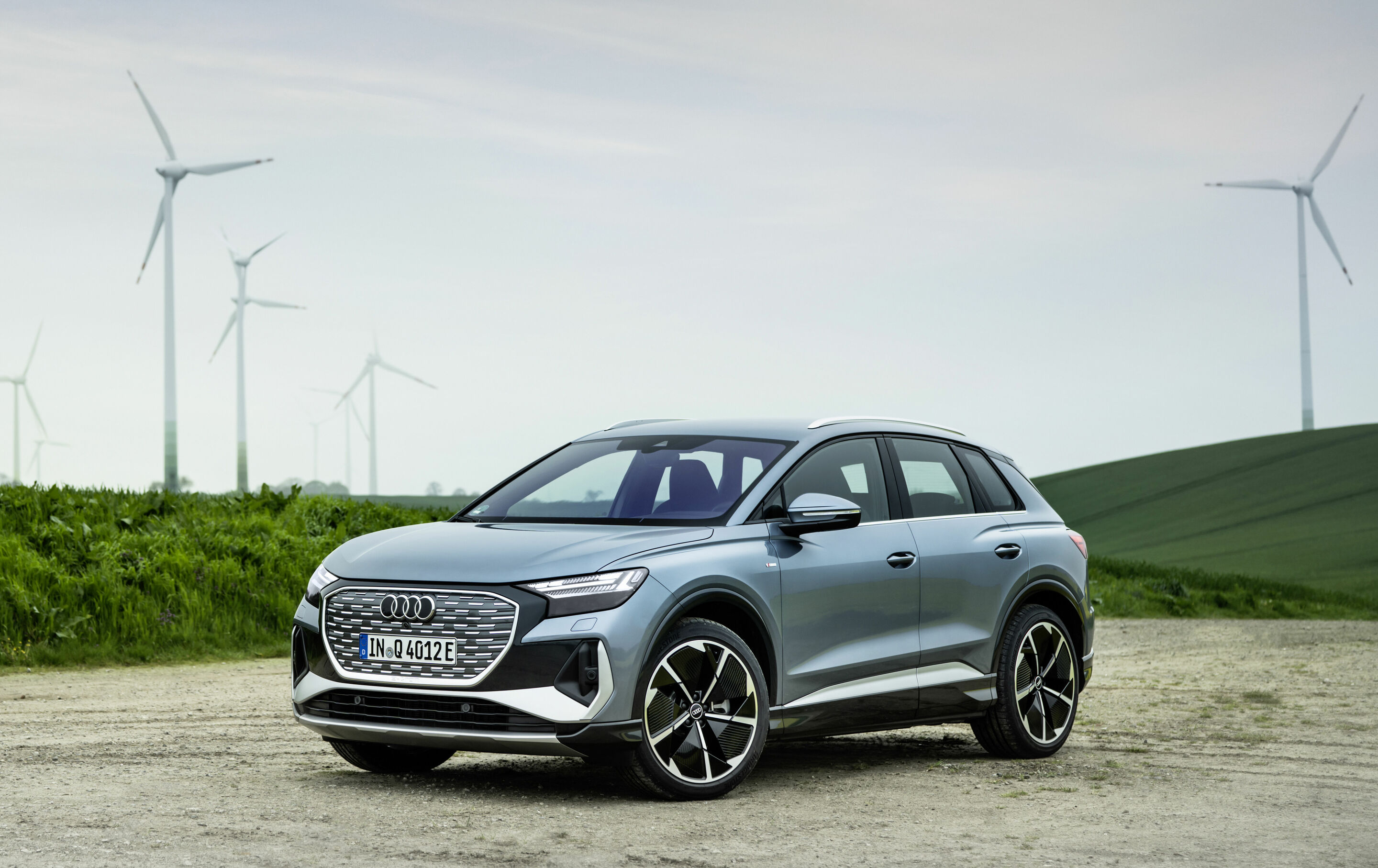
Audi Q4 e-tron
Audi Q4 e-tron
The Audi Q4 e-tron is being comprehensively upgraded: with a retuned chassis, increased efficiency, characteristic sound, and more standard equipment. In addition to an optimized drive concept and higher charging power, Audi is expanding the range of functions in the model's driver assistance system. With the optional adaptive driving assistant, it now supports lane changes.
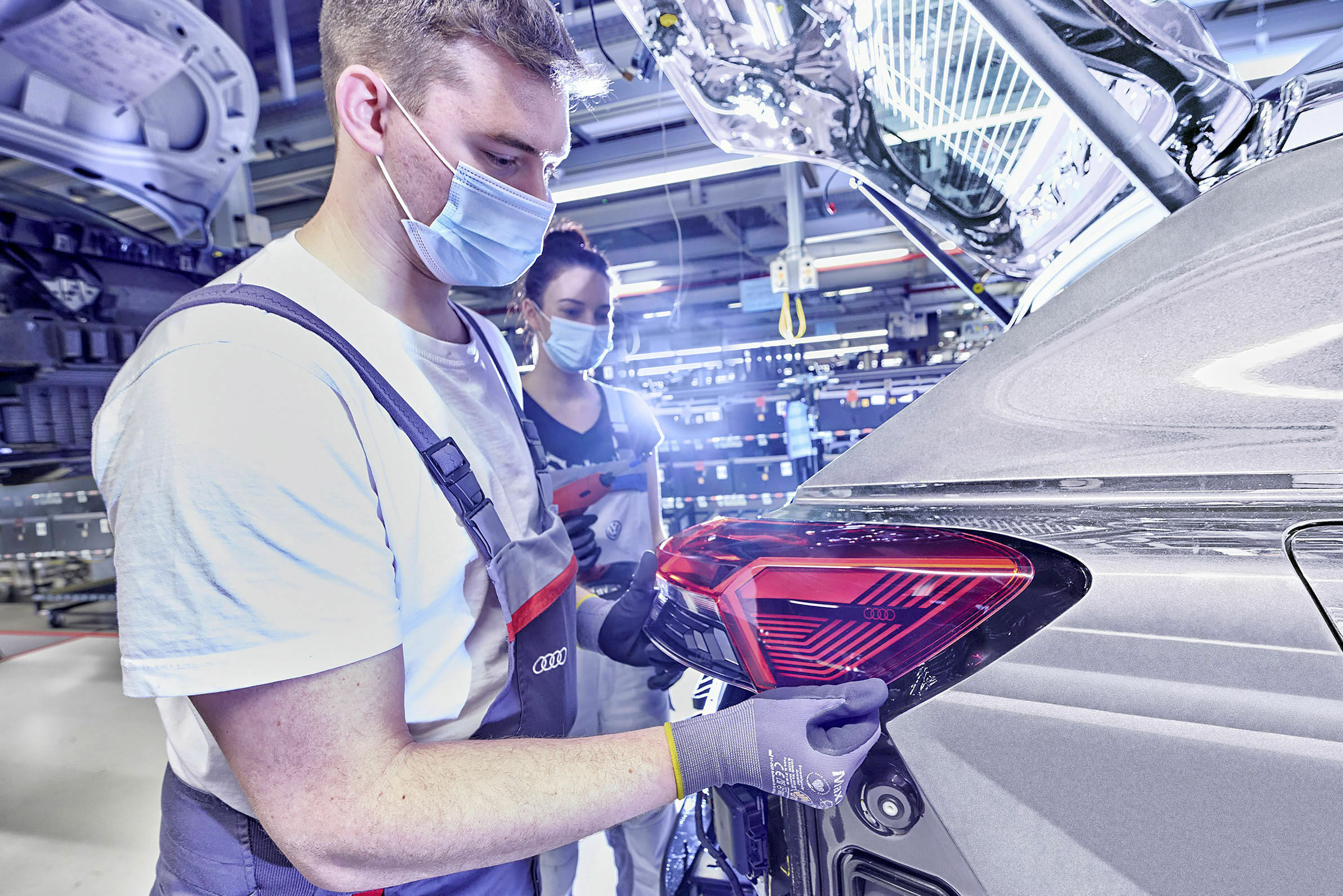 Start of production for Audi Q4 e-tron
Start of production for Audi Q4 e-tron
The Audi Q4 e-tron is being launched in the highly attractive and growing market segment of compact SUVs. For Audi customers, it offers an entry into the world of electric premium mobility at an attractive price. Not only does the compact model offer almost as much space in its interior as a full-size SUV, but the display concept featuring an optional augmented-reality head-up display is also pioneering in its class. Production of the Q4 e-tron will be carbon-neutral right from the start. The Zwickau plant purchases energy from renewable sources only and has a highly efficient combined heat-and-power plant. Audi is also working to further minimize CO2 emissions in the value chain. When the Audi Q4 e-tron reaches the end of its life cycle, its battery is to be used in second-life concepts or recycled as a source of raw materials.

Wireless software updates for the first time via future over-the-air interface Expanded portfolio with additional connect functions for on-board and the myAudi app Optimized DC charging power and Plug and Charge for even more convenient on-the-road charging
Audi is continuing to systematically advance the Q4 e-tron and Q4 Sportback e-tron. Audi is updating all vehicles from the start of series production up to and including the 2022 model year with software version 3.2. This new software comes now as standard in series production for the current 2023 model year. Foremost among the new functions with high everyday utility is the option of performing future software updates via a wireless over-the-air interface.
The software update for the Q4 e-tron and Q4 Sportback e-tron also allows users to create personal profiles. Another new feature: Users can use the e-tron route planner in the myAudi app to plan a route and send it to their Q4 e-tron. The new software version also saves navigation data such as recent destinations. The myAudi app can be used to locate the car’s parking position as well as to check a variety of status messages. Should the car break down or be involved in a fender bender, the driver will be able to use the online roadside assistance call with Audi damage service going forward. Improved charging power at home and on the road The software update also offers added value when charging at home or on the road. The “Preferred charging time” function helps customers charge at low-cost times, e.g. at night, with a variable-rate electricity plan. It works by allowing the user to set up a defined charging window. And timers in the car and the myAudi app make charging with alternating current (AC) even more convenient now too.
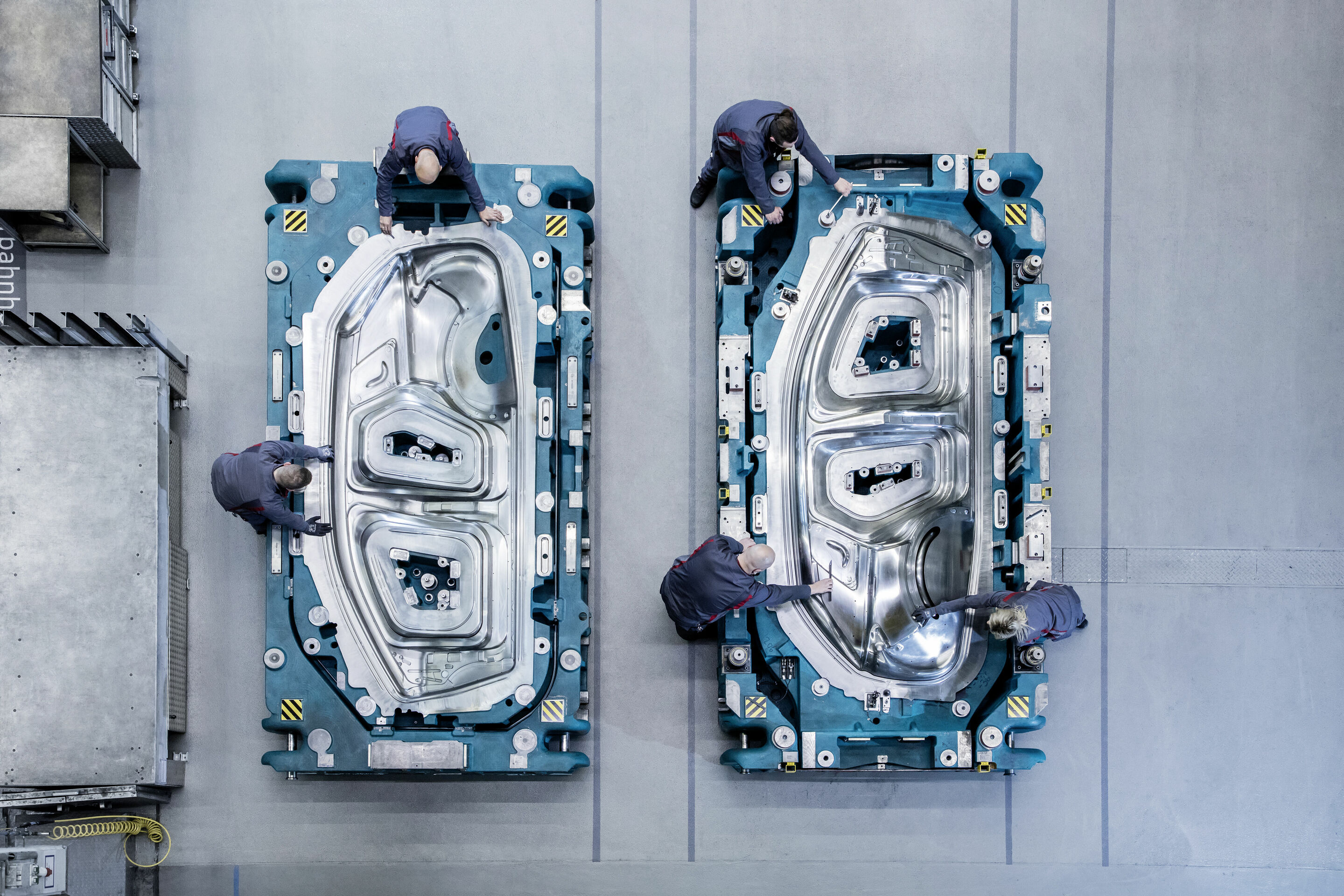 Precision in every detail: Toolmaking translates the emotional design of the Audi Q4 e-tron into sheet metal
Precision in every detail: Toolmaking translates the emotional design of the Audi Q4 e-tron into sheet metal
The EV offensive picks up speed: The Q4 e-tron launches in a dynamic market segment Audi’s electric offensive continues to pick up steam, with the Q4 e-tron following in the footsteps of the large Audi e-tron and e-tron Sportback SUV models as well as the high-performance e-tron GT. The Q4 e-tron plays a central role in the brand’s electrification strategy, launching in a particularly attractive and fast-growing market segment, the compact SUV class. For Audi customers, it offers a competitively priced entry into the world of premium electric mobility. Note for journalists:The world premiere of the Audi Q4 e-tron will be broadcast on the AUDI AG channels on April 14th. You will then find extensive press material in the Audi MediaCenter
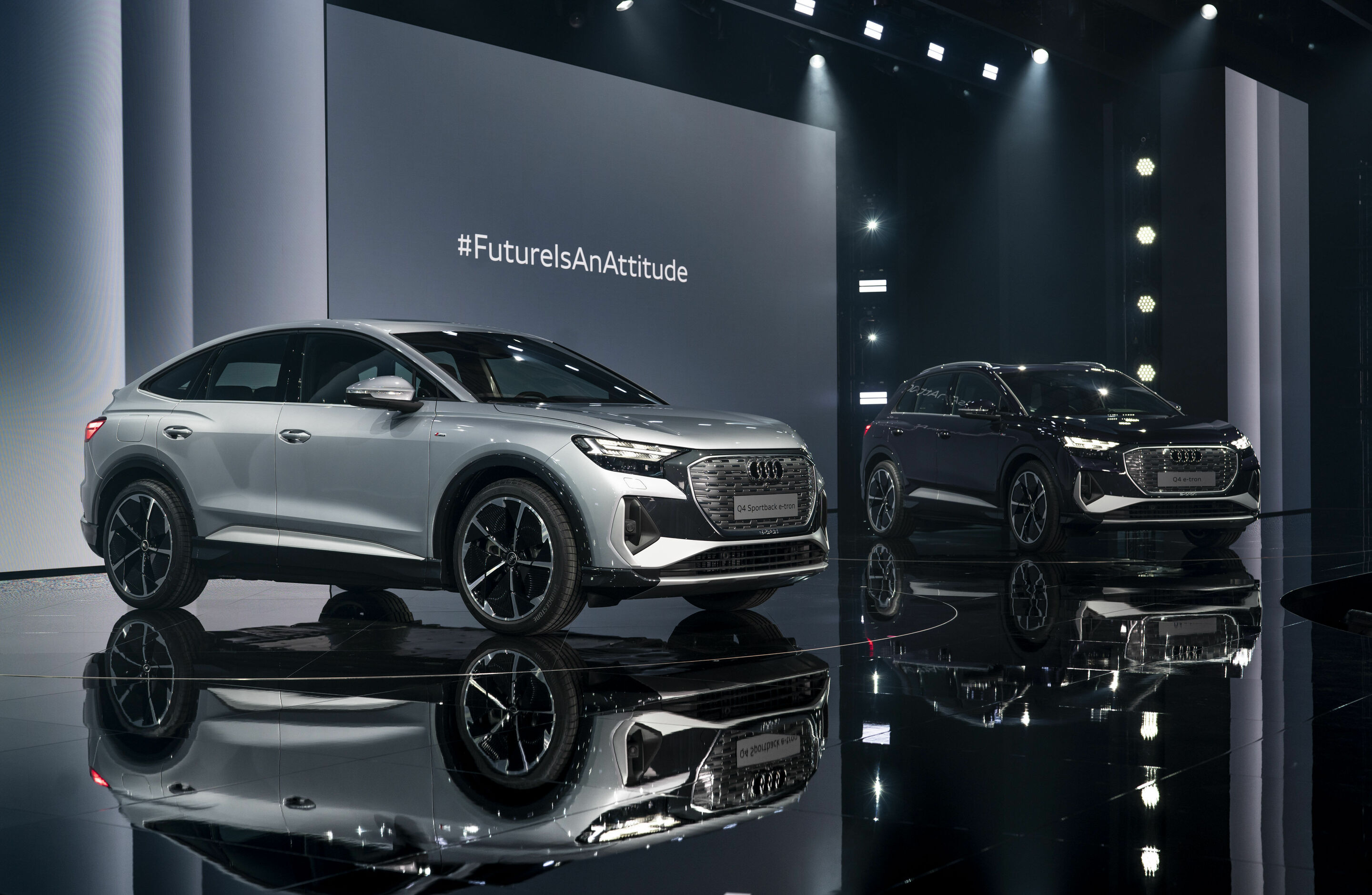

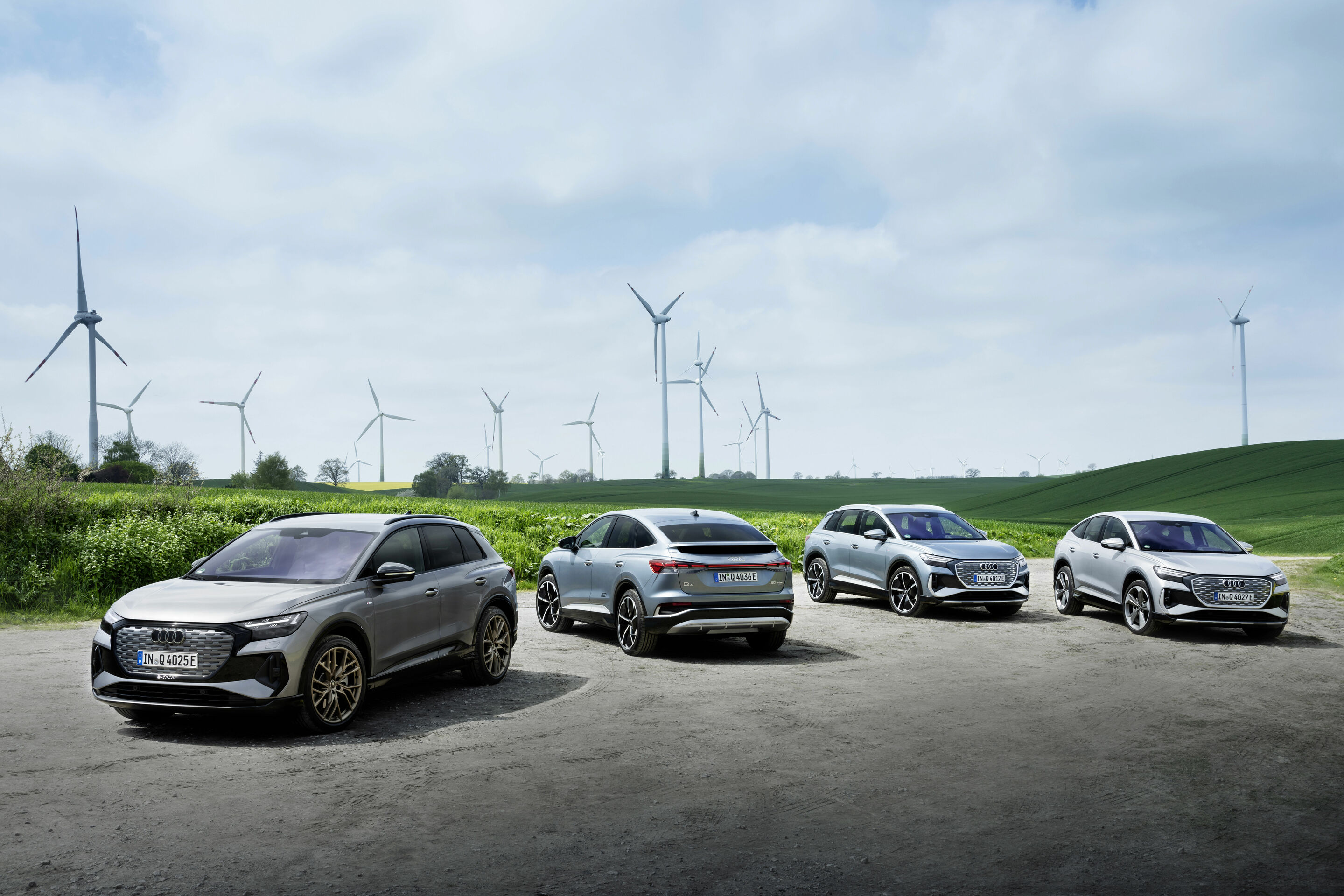
Versatile all-rounders for everyday use that transfer the progressive design of the concept cars into series production and that can be driven locally without any emissions: The Audi Q4 e-tron and the Q4 Sportback e-tron are the first compact electric SUVs from the brand with the Four Rings.
Both of them impress with a new spacious dimension in the interior and pioneering solutions when it comes to operation, display, and assist systems. The augmented reality head-up display connects the virtual and the real worlds in a totally new way. The range comprises three drive versions, spearheaded by a quattro model with a maximum output of 220 kW (299 PS)(Maximum output determined according to UN-GTR.21.). Attributes that they all share are zero local emissions driving and high ranges, charging times of around ten minutes for sufficient power to travel about 130 kilometers (80.8 mi) in ideal conditions (WLTP) and convenient charging with the e-tron Charging Service. The rear-wheel drive Q4 40 e-tron achieves a range of up to 520 kilometers (323.1 mi) in the WLTP cycle. It goes on sale in Europe in June 2021, with prices in Germany starting at EUR 41,900 – where the customer can claim a subsidy of EUR 9,000 (net). Discover extensive information in our multimedia press kit.
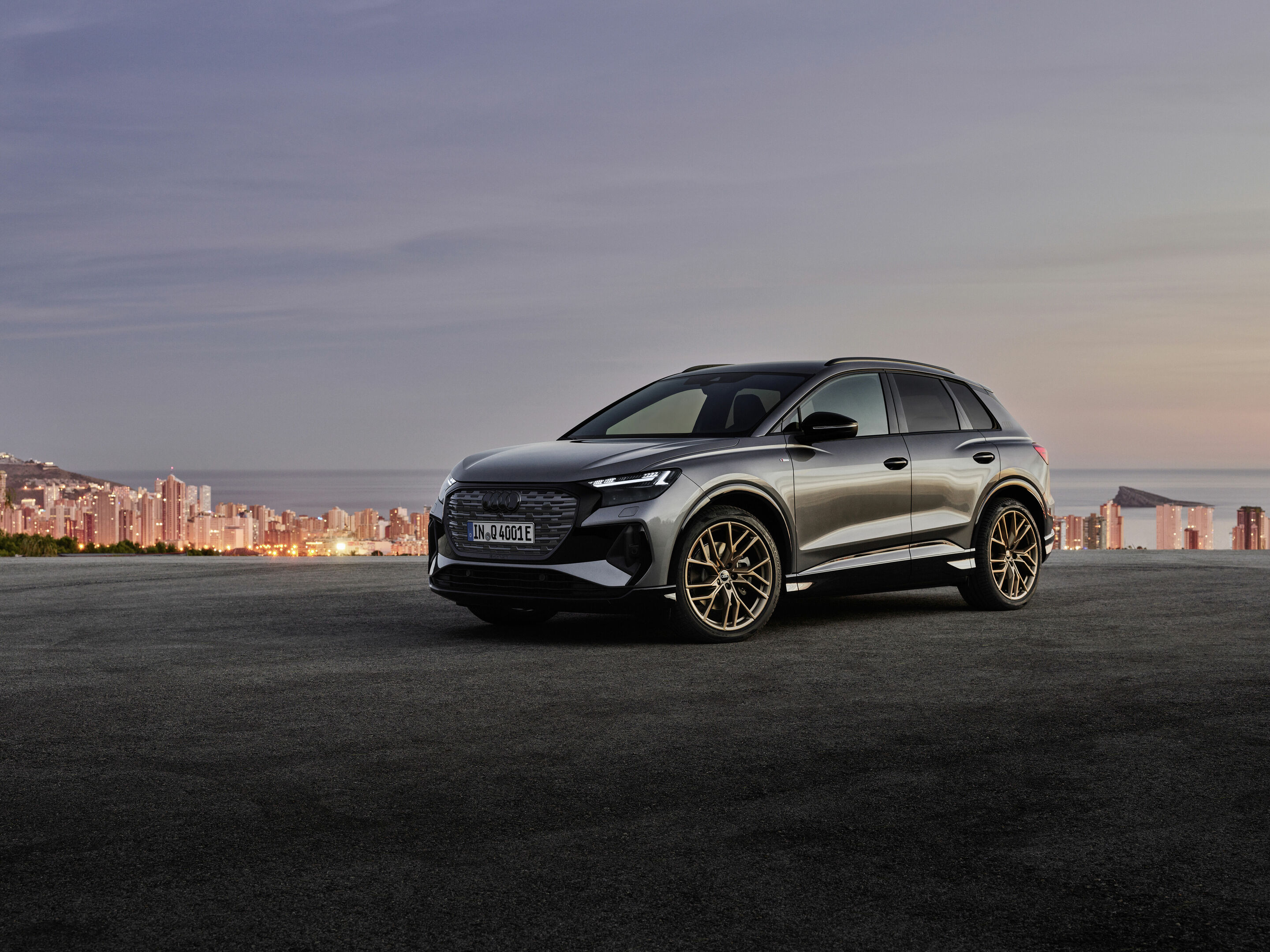
 A new dimension of e-mobility: the Audi Q4 e-tron sets a benchmark for interior and operation
A new dimension of e-mobility: the Audi Q4 e-tron sets a benchmark for interior and operation
In a set of seats for the Q4 e-tron, 26 1.5-liter plastic bottles are given a new purpose. Audi goes electric: the Q4 e-tron is being launched in a dynamic market segment The electric offensive at Audi continues to pick up steam. The Q4 e-tron follows the large SUV models e-tron and e-tron Sportback, as well as the sporty e-tron GT. The Q4 e-tron plays a key part in the brand’s electrification strategy. It is being launched in a particularly attractive and fast-growing market segment, the class of compact SUVs. For Audi customers, it offers an entry into the world of electric premium mobility at an attractive price.
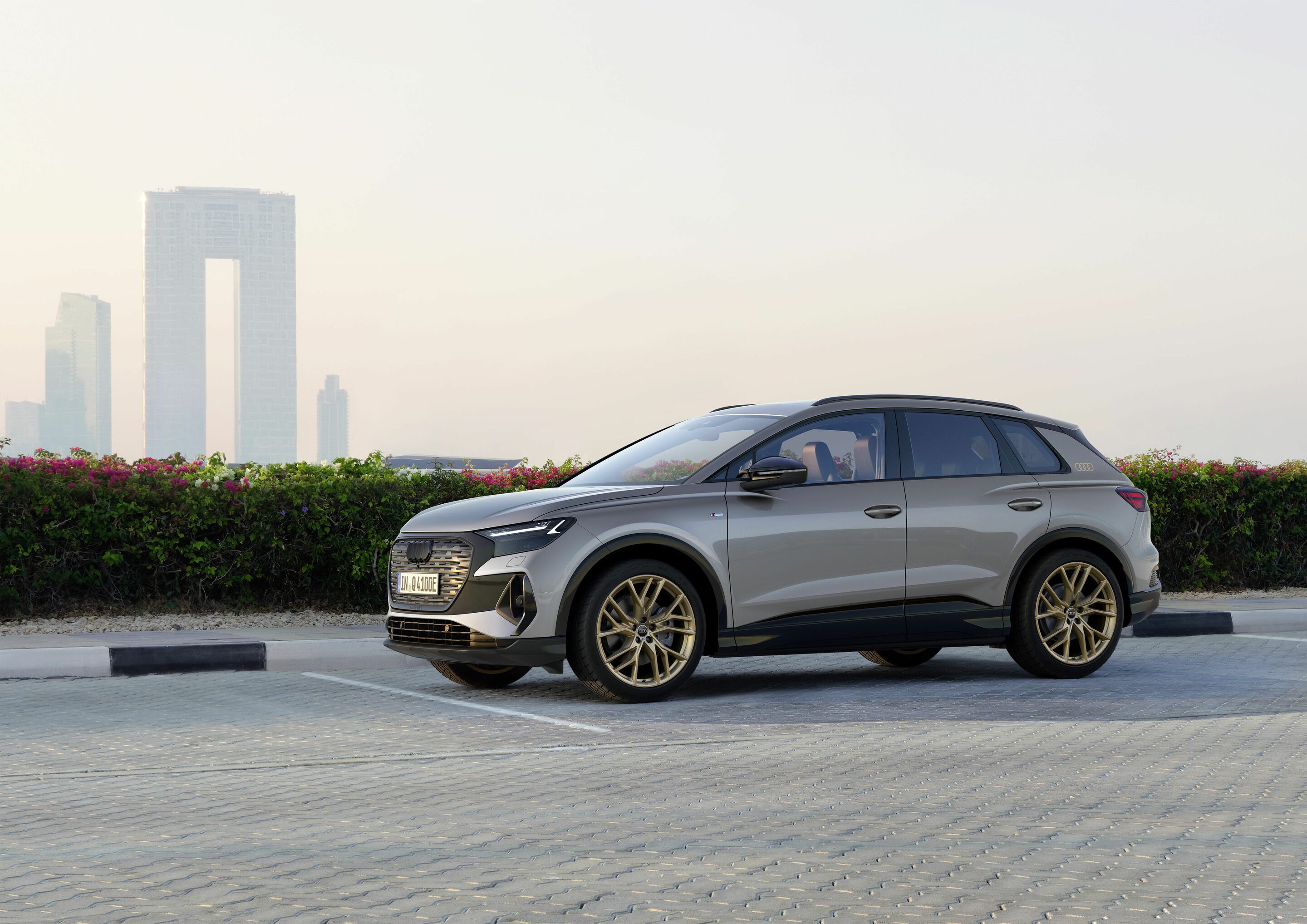 Update for the Audi Q4 e-tron: more range, more efficiency, more emotions
Update for the Audi Q4 e-tron: more range, more efficiency, more emotions
New drive system with higher efficiency and more power For both rear-wheel drive and quattro all-wheel drive, all Audi Q4 e-tron models now feature a permanently excited synchronous machine (PSM) on the rear axle. The update gives gives the Audi Q4 e-tron model family a completely redeveloped PSM notable for its higher efficiency and greater power. The models benefit from an increased range and superior power delivery. a completely redeveloped PSM notable for its higher efficiency and greater power. The electric SUV benefits from an increased range and superior power delivery. The Audi Q4 Sportback 45 e-tron, for example, reaches a range of up to 562 kilometers (349 mi) in the WLTP cycle. The Audi Q4 45 e-tron and the Audi Q4 Sportback 45 e-tron with rear-wheel drive produce 210 kW (286 PS) and accelerate from zero to 100 km/h (62 mph) in 6.7 seconds. The Audi Q4 45 e-tron quattro and the Audi Q4 Sportback 45 e-tron quattro with 210 kW (286 PS) take 6.6 seconds.









