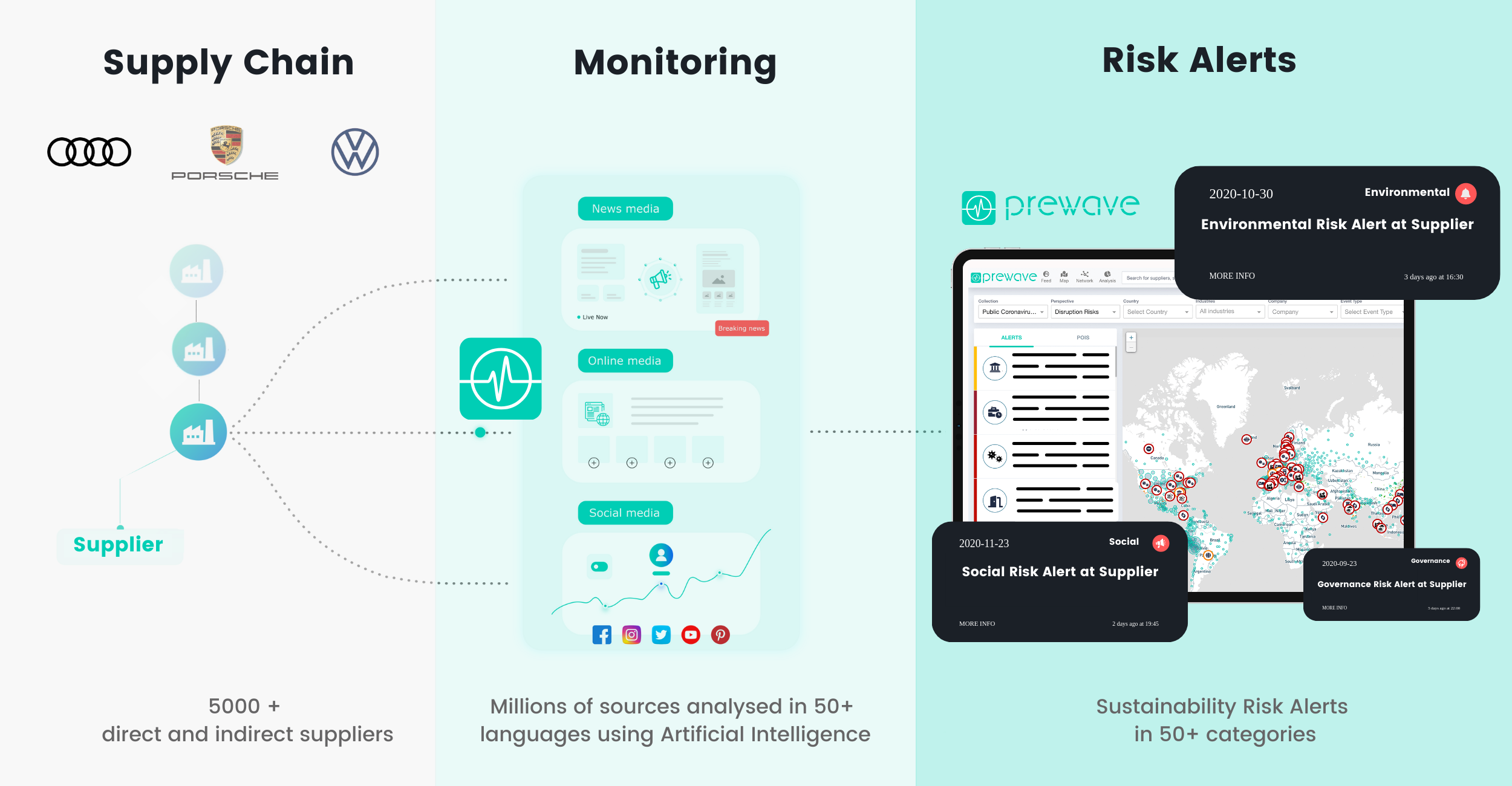
Supply chain monitoring:
Audi uses artificial intelligence (AI) for sustainability
- AI as a risk radar: intelligent early warning system analyzes publicly available sources in more than 50 languages for sustainability risks in the supply chain
- Early detection of environmental, human rights, and compliance violations with the help of AI
- Audi testing how suppliers meet the required sustainability criteria within the scope of a pilot project since October 2020
The automotive manufacturing supply chain is complex. This makes it all the more important to understand potential risks and identify correlations at an early stage. Since October 2020, intelligent algorithms have been analyzing news about suppliers from publicly available online media sources and social networks as part of a pilot project being conducted in around 150 countries worldwide. This analysis encompasses sustainability criteria such as environmental pollution, human rights violations, and corruption. If there is any suspicion of potential sustainability violations, artificial intelligence sounds the alarm.
Audi intends to further intensify its sustainability activities in the future through digital supply chain monitoring. Ensuring that its own sustainability requirements are also met by all the companies involved within the supply chain is extremely important to the automaker. Audi’s direct suppliers are, in turn, obligated to ensure that their suppliers also comply with these requirements. This sustainability radar is designed to uncover violations at an early stage and initiate appropriate consequences.
Digital early warning radar for the supply chain
Audi has outlined its sustainability requirements for business partners in its “Code of Conduct for Business Partners.” Audi takes well-founded indications of violations extremely seriously and follows up with them systematically. Its defined environmental, social, and compliance guidelines form the basis for collaboration and are an integral part of the automaker’s risk assessment processes. A sustainability rating (“S rating”) for suppliers has been a mandatory criterion for awarding contracts since 2019. Audi uses this procedure to verify whether its contractual partners comply with the requirements laid out in the Code of Conduct for Business Partners. Audi only works with companies that pass this audit. In 2020, more than 13,000 suppliers provided the Volkswagen Group with a self-assessment of their own sustainability performance. More than 800 suppliers were audited on site, and more than 1,300 have improved their sustainability performance and now meet Audi’s stringent standards. Audi’s more than 14,000 direct suppliers from around 60 countries are also expected to ensure that their upstream partners comply with the sustainability requirements laid out in the Code of Conduct for Business Partners. In order to verify compliance with the requirements of the S rating, Audi also maintains several traditional complaint channels. These include, for example, more traditional channels such as post office boxes and ombudsmen. Artificial intelligence has supplemented supply chain monitoring at Audi since October 2020, thus complementing the traditional complaint channels with a proactive tool. “In order to handle the complexity of our supply chains in a responsible manner, we rely on strong alliances and new technologies,” says Susanne Lenz, supply chain sustainability strategist at Audi. Comprehensive risk monitoring at Audi combines different methods and systems – including with the aim of responsibly managing complexity in the supplier structure.
AI software: monitoring in 50 languages and 150 countries
The digital early warning system for sustainability risks used by Audi together with Volkswagen and Porsche collects publicly available news in more than 50 languages and from around 150 countries. This includes social media channels such as Twitter or YouTube as well as local news outlets. Since the AI developed by Austrian start-up Prewave uses automatic speech recognition to understand the meaning of the respective messages, potential sustainability violations can be identified flawlessly. “We are delighted to be working with Audi, Volkswagen, and Porsche to carry out this flagship project in the automotive industry. Our technology is being used to screen thousands of globally distributed suppliers for sustainability risks in real time. Machine learning and automated language processing thus makes possible what would be impossible to do manually – perform continuous risk assessments across the entire supply chain that Procurement can then use to proactively approach suppliers,” says Harald Nitschinger, CEO of Prewave. And because the intelligent algorithms are constantly learning, the system is continuously improving, and its ability to recognize indications of developing risks is increasing. But the main advantage of the AI used by Audi is the speed at which it recognizes relevant information online and transmits it in packaged form. “Because we receive indications earlier, we can assess potential sustainability risks to our supply chain in a timely manner and respond quickly,” says Lenz.
AI with a wide range of applications including social issues, the environment, and cybercrime
The AI covers a wide range of different areas – in the “Social” category, for example, it focuses on violations of labor law, unrest in the workforce, child labor, or discrimination in the workplace. Relevant criteria in the “Environment” category draw on public data regarding, among other issues, air pollution, water pollution, water consumption, or waste problems. And when it comes to topics such as cyber risk, the AI analyzes reports indicative of suspected cyberattacks, data fraud, or data theft. Whenever the AI detects a potential sustainability risk developing, Audi is notified automatically. Those responsible at the automaker then examine the situation in more detail. If the information received is correct, appropriate action is taken.
AI as an enabler of sustainability
This means that Audi, Volkswagen, and Porsche can, if necessary, demand the partner immediately initiate improvements or even completely terminate the business relationship. “Artificial intelligence and machine learning are becoming enablers of sustainability at our company,” says board member Dirk Große-Loheide, who is responsible for procurement and IT at Audi.
A powerful tool for greater transparency in the supply chain
The reliability and predictive capability of the installed software is currently being verified at more than 4,000 supplier companies. Initial results indicate that the AI used at Audi is suitable for responding quickly and effectively to the dynamic risks in supply chains, which change daily. “Analyzing massive amounts of data using artificial intelligence highlights how digitalization can uncover risks in our supply chain. Thanks to our collaboration with Prewave, we are using an adaptive, powerful tool to increase transparency and efficiently monitor sustainability agreements,” sums up Lenz.
The use of AI in supply chain monitoring also gives Audi a clear competitive advantage – according to a study conducted by Capgemini in early 2021 that surveyed customers in Germany, the United Kingdom, and the United States, nearly 70 percent of car buyers view sustainability as an important factor in their purchase decision.