Search
All search results for "dynamic all-wheel steering"
(224)
 Audi Q3
Audi Q3
Audi Q3
The new Audi Q3 is our impressive all-rounder in the compact segment. Now in its third generation, the SUV stands out with its dynamic, muscular look. As a digital companion for everyday life, the Q3 is ideally equipped to deliver an inspiring driving experience thanks to its modern driver assistance systems and lighting technology from the full-size class. On the inside, the modern steering wheel control unit enables a new operating experience and creates even more storage space and a more spacious feel.
 Improved handling: progressive steering and all-wheel steering
Improved handling: progressive steering and all-wheel steering
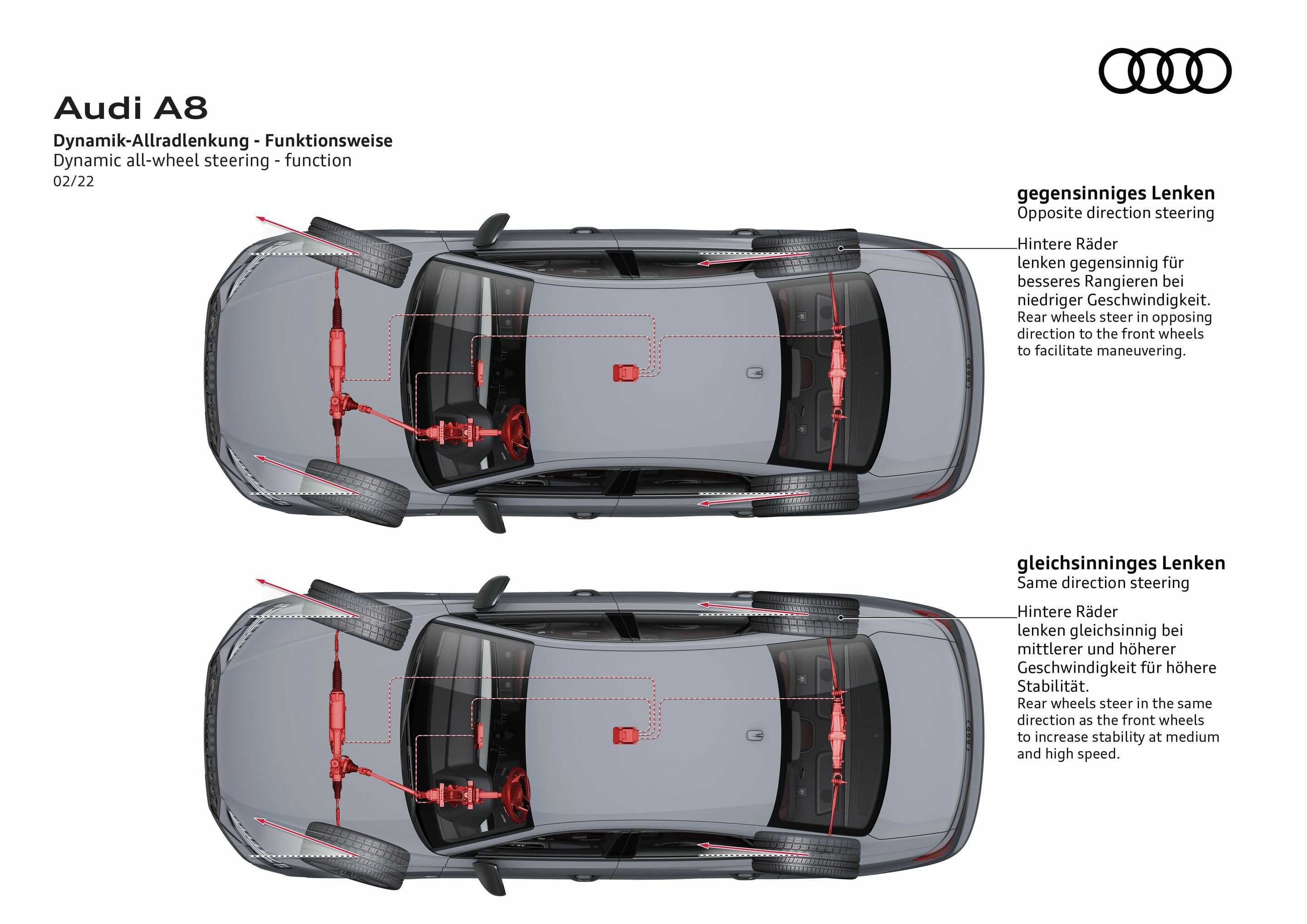
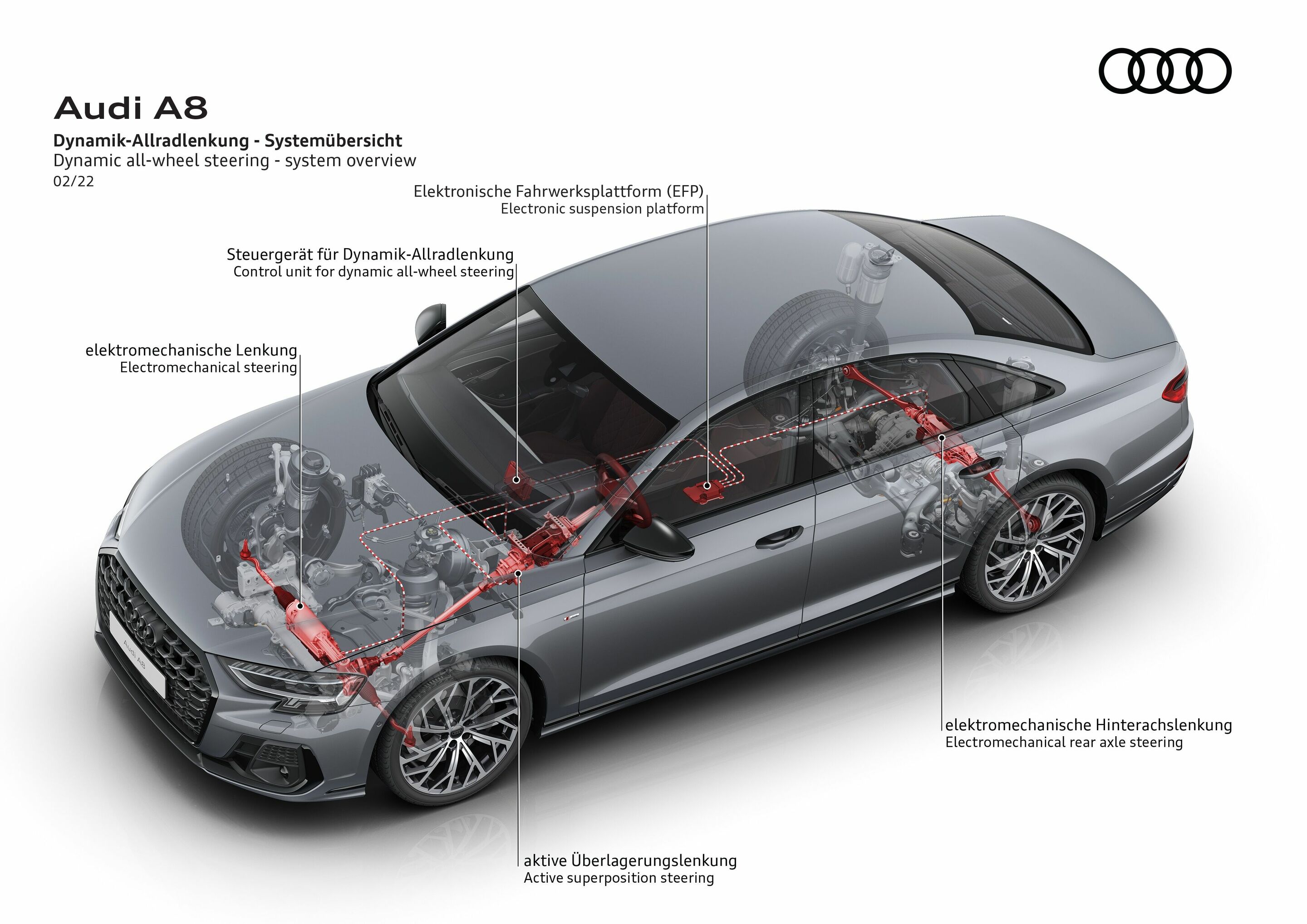
The reworked and now more direct steering contributes significantly to the comfortable yet equally dynamic handling of the new A6 Avant. Compared to its predecessor, the entire path from the steering wheel to the wheels is designed to be stiffer. This includes the torsion bar at the steering gear, the rigidly bolted steering rack, and the stiffer control arm bushings. Camber on the front axle has also been slightly increased. All in all, these measures result in a noticeably improved steering response and more feedback from the road, which makes for precise and light-footed vehicle handling. The A6 Avant comes standard with electromechanical progressive steering. The steering ratio varies depending on the steering angle: at small steering angles, such as on the highway, the steering is more indirect to prevent any nervous behavior from influencing the steering. At larger steering angles, the ratio is increasingly more direct, reducing the amount of physical effort required to steer in city traffic and when parking. Moreover, the progressive steering provides a sporty driving feel in tight corners. The Audi drive select dynamic handling system can be used to vary the steering characteristics – specifically steering weight – in several modes. All-wheel steering is optionally available in conjunction with quattro all-wheel drive. It works with a dynamic function whose reaction speed has been improved even further. At speeds of up to roughly 60 km/h (37.3 mph), the rear wheels turn up to five degrees in the opposite direction to the front wheels. This decreases the turning circle by up to one meter (39.4 in), reducing it to 11.3 meters (37.1 ft). The car is thus more agile in city traffic and in tight curves. At medium and higher speeds, the rear wheels turn in the same direction, enabling stable and even more precise handling. The equipment, data and prices specified in this document refer to the model range offered in Germany.
 Fine-tuning the characteristics of the Audi steering system
Fine-tuning the characteristics of the Audi steering system
Interview with driving characteristics developer Carsten Jablonowski Basic calibration carried out virtually to create the typical Audi steering feel Different steering systems build on each other
Whether driving on winding roads in the Alps, a busy highway, or city streets filled with potholes on the way to the supermarket – a good steering wheel has to cover the entire spectrum of driving situations. In this interview, Carsten Jablonowski, Driving Characteristics Development Team Lead, explains the complex process of fine-tuning the chassis and steering, which is what gives an Audi its unique steering feel.
Mr. Jablonowski, how would you describe the typical Audi steering feel? When we’re behind the wheel of a car, its individual steering feel depends on a variety of factors. Among other factors, the overall design, vehicle weight and weight distribution play a role, as do the individual chassis components, the tires, and the steering system used. Now when I get into different Audi models, I get that familiar feeling after only a short time – the car steers effortlessly, smoothly, and precisely with little effort. And this is true regardless of whether I’m parking, driving through hairpin bends, or simply cruising around the city. Because an Audi steering wheel generates greater torque, I’m able to negotiate curves precisely and with agility. Our models change direction with a high degree of precision, especially when driving fast through alternating turns. On the other hand, an Audi will smoothly drive straight ahead at fast highway speeds and isn’t jittery at all. This means I can always feel how the car is interacting with the road. The steering wheel gives me direct feedback regarding the car’s balance, level of grip, and road unevenness such as bumps and ruts. All in all, this is important for a safe and pleasant driving experience. The vehicle development process takes up to five years.
 Audi A6 Avant e-hybrid quattro
Audi A6 Avant e-hybrid quattro
Audi A6 Avant e-hybrid quattro
With a system output of up to 270 kW, an electric range of up to 106 kilometers (65.9 mi), standard all-wheel steering, and optimized aeroacoustics, the Audi A6 Avant e-hybrid quattro delivers a sporty and comfortable driving experience with plenty of freedom for everyday flexibility. It also comes with extensive standard equipment.
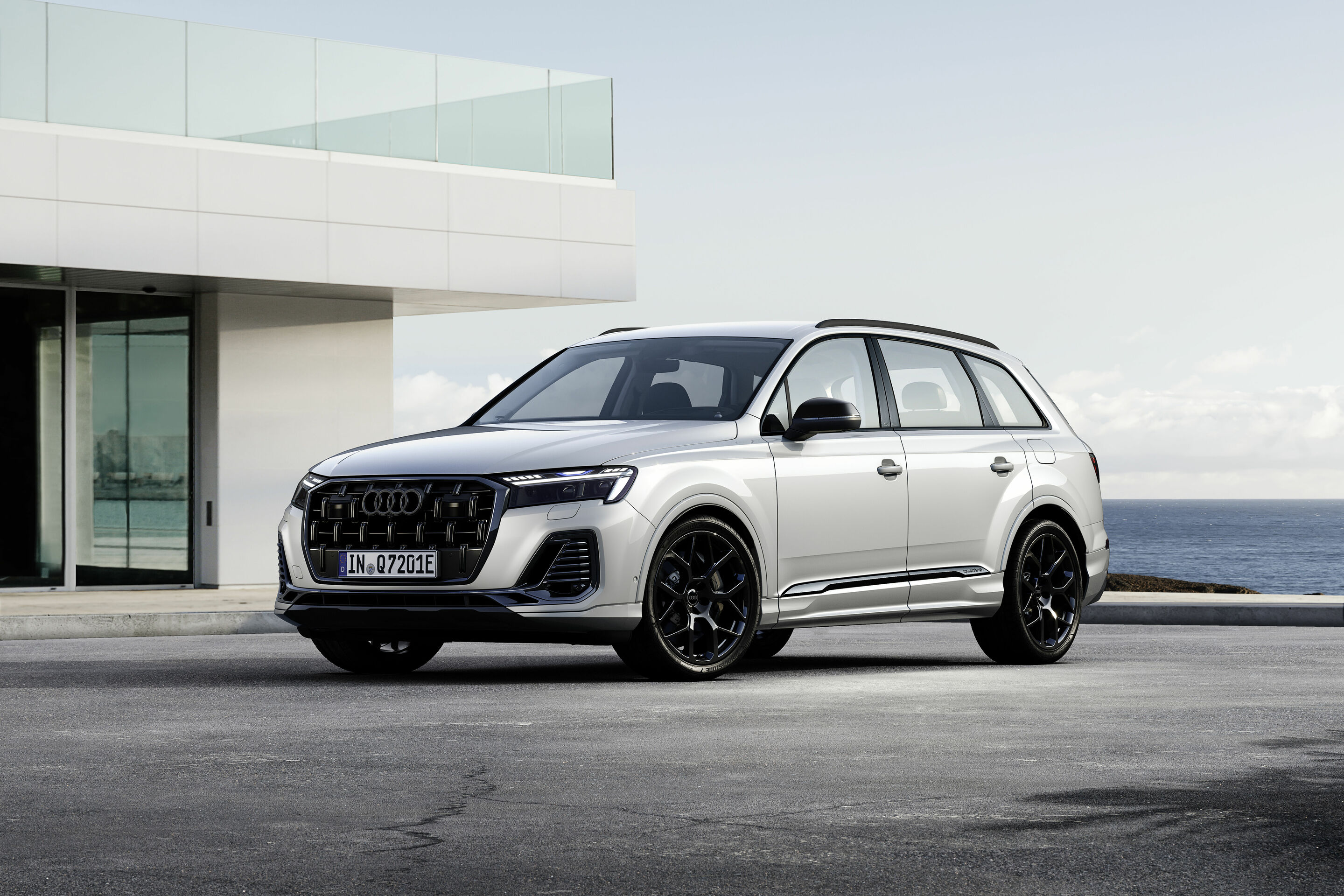 Audi Q7 TFSI e quattro
Audi Q7 TFSI e quattro
New options include all-wheel steering and electromechanical active roll stabilization (eAWS) for a dynamic driving experience.
Images
Engine type V6 engine
Displacement in cc / bore x stroke in mm / compression 2995 / 84.5 x 89.0 / 11.2
Max. power output in kW (PS) / at rpm 250 (340) / 5200 - 6400
Max. torque in Nm (lb-ft) / at rpm 500 (368.8) / 1370 - 4500
Top speed / electrical in km/h (mph) 240 (149.1) (limited) / 140 (87.0)
System acceleration, 0-100 km/h (0-62.1 mph) 5.7
Electrical range, combined (EAER) in km (mi) 80 - 84 (49.7 - 52.2)
Electric power consumption, weighted combined in kWh/100 km (62.1 mi) 29.1 - 27.8
Fuel consumption, weighted combined in l/100 km (US mpg) 1.4 - 1.2 (168.0 - 196.0)
CO2 emissions, weighted combined, in g/km (g/mi) 33 - 28 (53.1 - 45.1)
CO2 class, weighted combined B
CO2 class with discharged battery G
Unladen weight without driver / with driver / gross weight limit in kg (lb) 2385 (5258.0) / 2460 (5423.4) / 3100 (6834.3)
Engine type V6 engine
Displacement in cc / bore x stroke in mm / compression 2995 / 84.5 x 89.0 / 11.2
Max. power output in kW (PS) / at rpm 250 (340) / 5200 - 6400
Max. torque in Nm (lb-ft) / at rpm 500 (368.8) / 1370 - 4500
Top speed / electrical in km/h (mph) 240 (149.1) (limited) / 140 (87.0)
System acceleration, 0-100 km/h (0-62.1 mph) 5.0
Electrical range, combined (EAER) in km (mi) 80 - 84 (49.7 - 52.2)
Electric power consumption, weighted combined in kWh/100 km (62.1 mi) 29.1 - 28.0
Fuel consumption, weighted combined in l/100 km (US mpg) 1.4 - 1.3 (168.0 - 180.9)
CO2 emissions, weighted combined, in g/km (g/mi) 33 - 29 (53.1 - 46.7)
CO2 class, weighted combined B
CO2 class with discharged battery G
Unladen weight without driver / with driver / gross weight limit in kg (lb) 2385 (5258.0) / 2460 (5423.4) / 3100 (6834.3)
 Audi A6 Sedan
Audi A6 Sedan
In combination with sophisticated suspension technologies, the A6 Sedan impresses with its qualities for everyday and long-distance driving: both the adaptive air suspension and all-wheel steering combine driving comfort and agile handling to the highest degree.
 Audi A6 Avant
Audi A6 Avant
Whether on long trips or city driving, the adaptive air suspension and all-wheel steering ensure a smooth ride and sporty handling in equal measure. Additional highlights include intuitive operating and infotainment concepts, new digital lighting technology, and intelligent driver assistance systems.
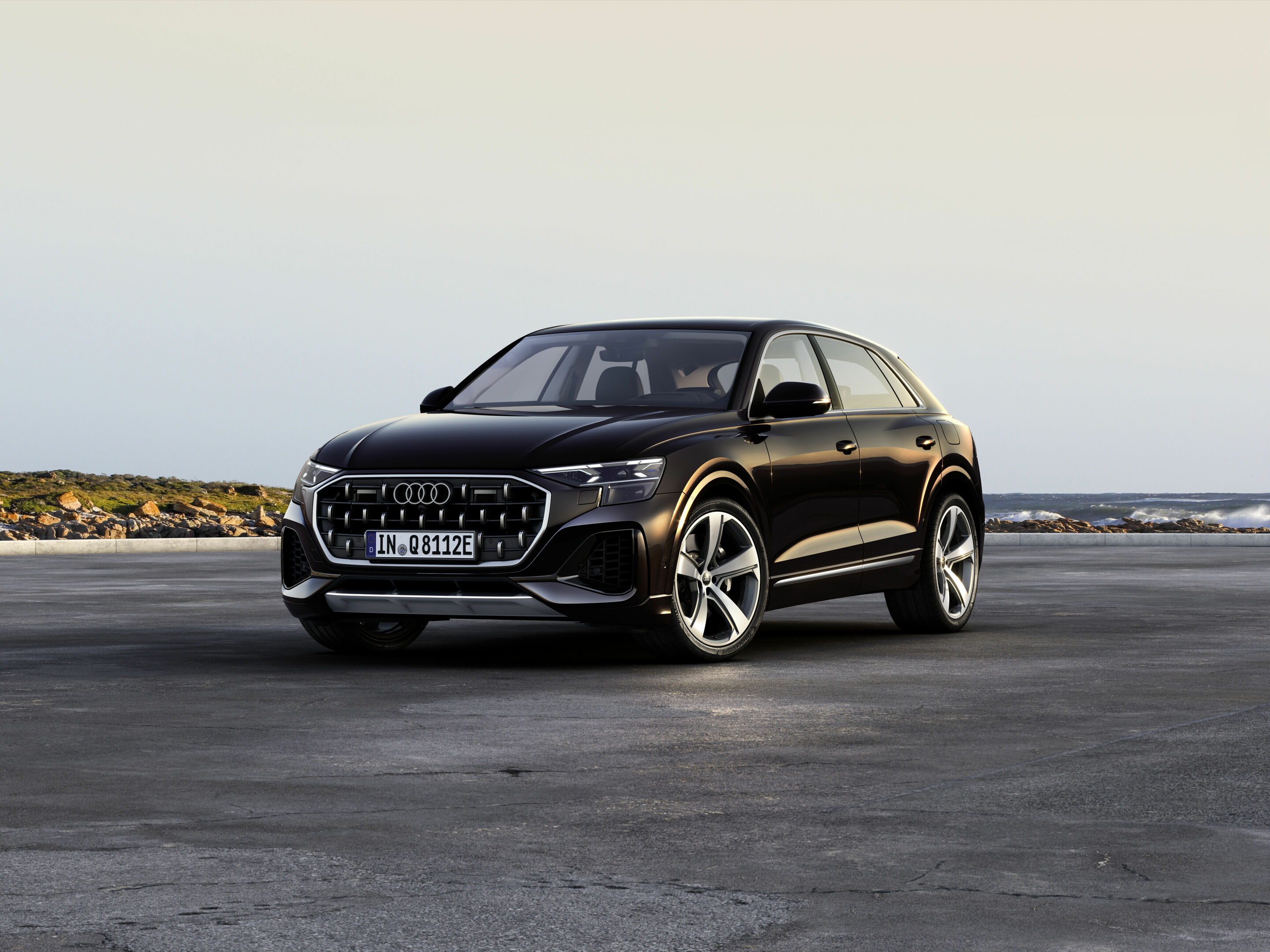 Audi Q8 TFSI e quattro
Audi Q8 TFSI e quattro
New options such as all-wheel steering and electromechanical active roll stabilization (eAWS) ensure a dynamic driving experience.