Audi Ingolstadt: net carbon neutral production since January 2024
- Production of the upcoming fully electric Audi Q6 e-tron series, as well as all other vehicles built at the site, will be net carbon-neutral
- Audi Board Member for Production and Logistics Gerd Walker: “By transitioning the Ingolstadt site to renewable energies, we are taking a major step toward our goal of net carbon-neutral vehicle production”
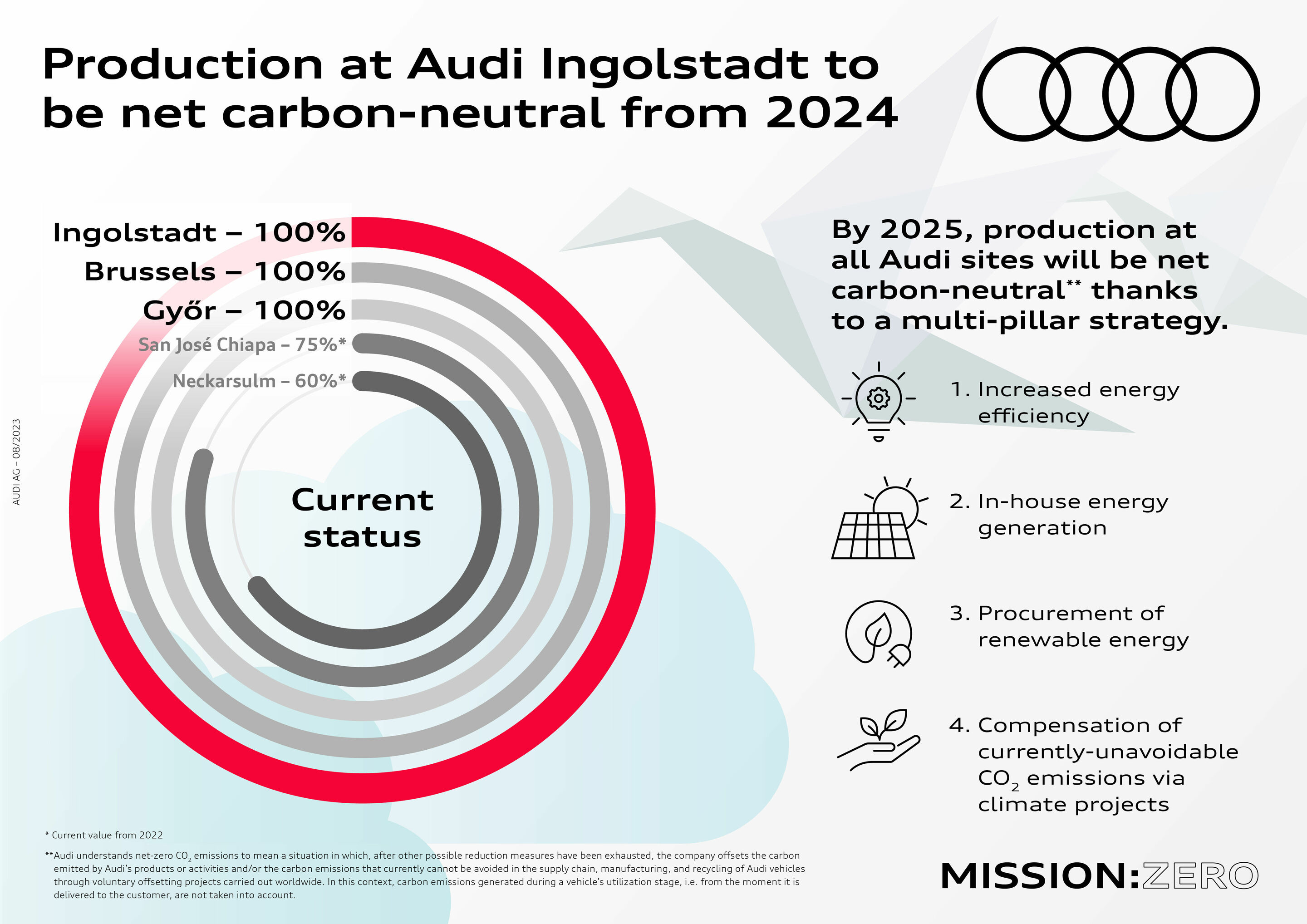
- As part of the environmental program Mission:Zero, all Audi sites will be net carbon-neutral by 2025
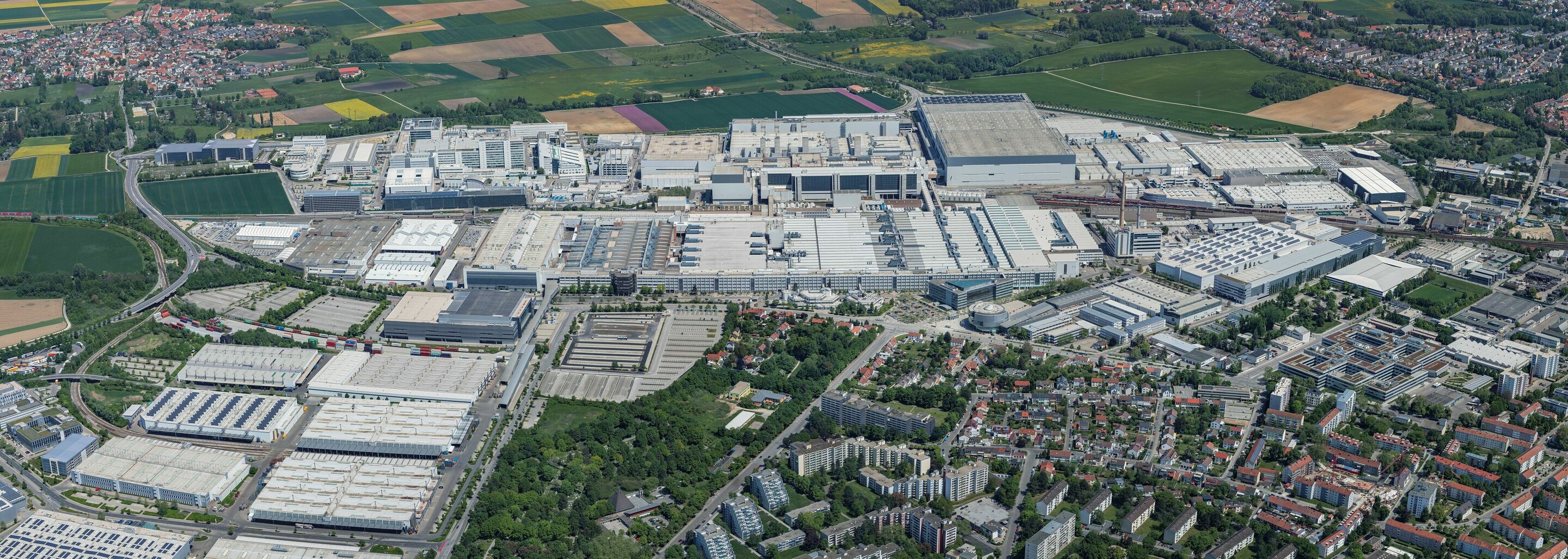
The Audi plant in Ingolstadt began net carbon-neutral production on January 1, 2024. After Brussels (Belgium, 2018) and Győr (Hungary, 2020), it is the third Audi plant to operate with net zero emissions. In addition are the Audi R8 and e-tron GT quattro models, which have been built at Böllinger Höfe with net zero emissions since 2020. As part of its Mission:Zero environmental program, Audi has set itself the goal of achieving net carbon neutrality at all its sites worldwide by 2025. By then, the final steps will have been taken in Neckarsulm and San José Chiapa (Mexico).
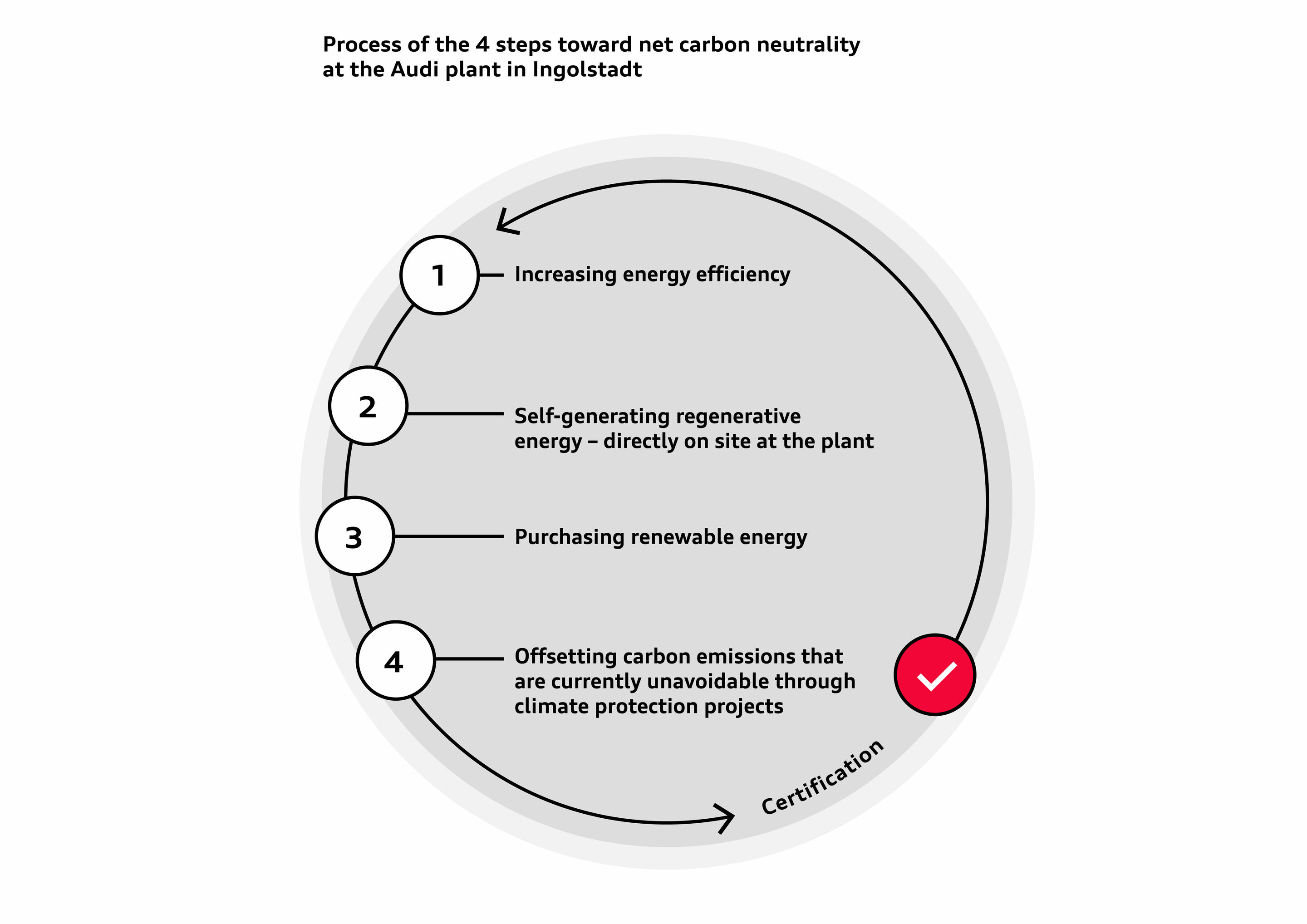
Audi Board Member for Production and Logistics Gerd Walker emphasizes: “Protecting the environment as best as possible is firmly anchored in Audi’s corporate strategy. By transitioning the Ingolstadt site to renewable energies, we are taking a major step toward our goal of net carbon-neutral1 vehicle production.” To achieve its ambitious goal, the brand with the four rings is implementing a four-pillar concept.
1. Increasing energy efficiency
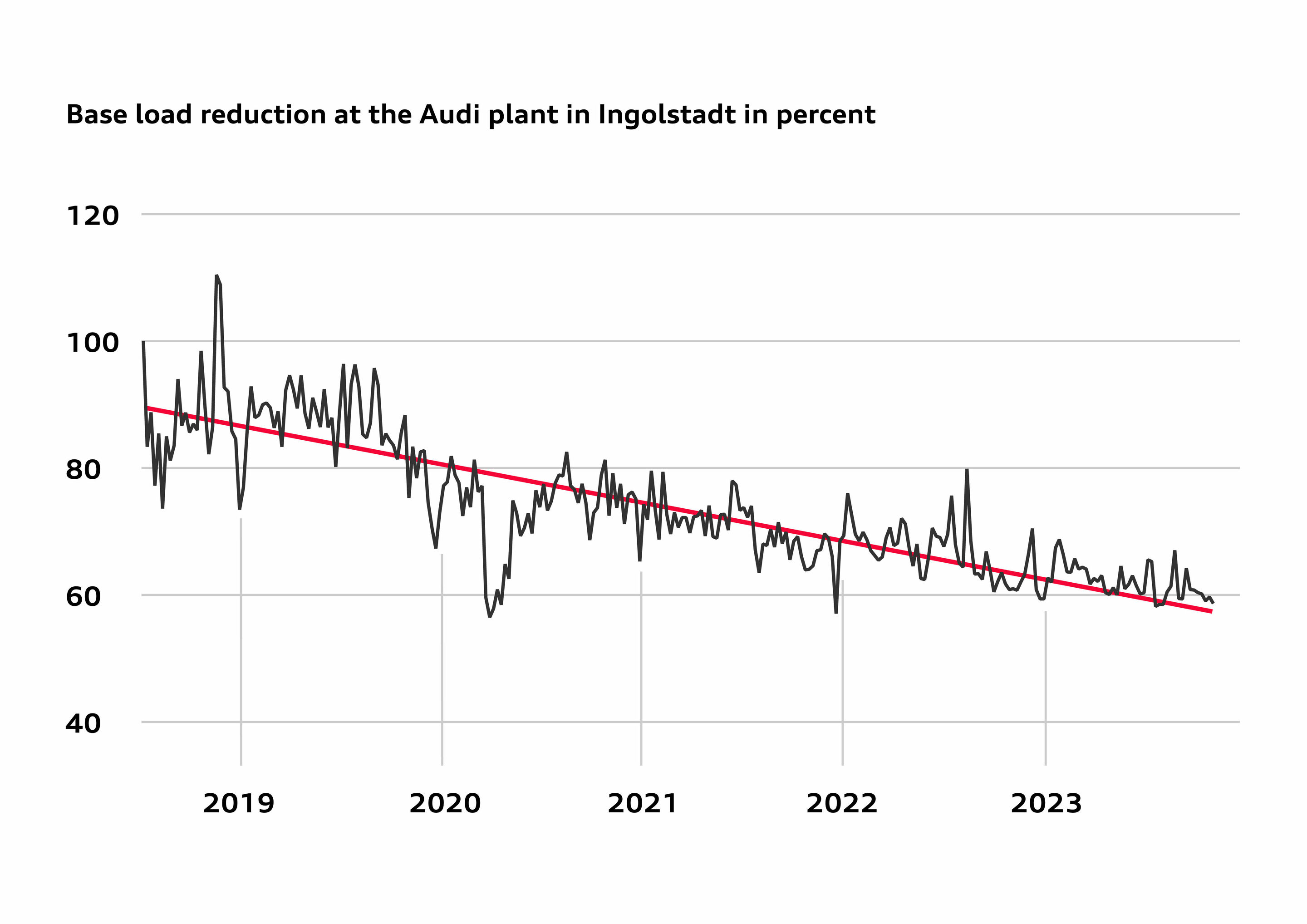
In the first pillar, Audi is improving energy efficiency at its sites, which will already avoid large amounts of carbon emissions. In 2022, for example, these energy management measures allowed the Ingolstadt site to save more than 35,000 megawatt hours of energy and prevent more than 5,000 tons of carbon emissions.
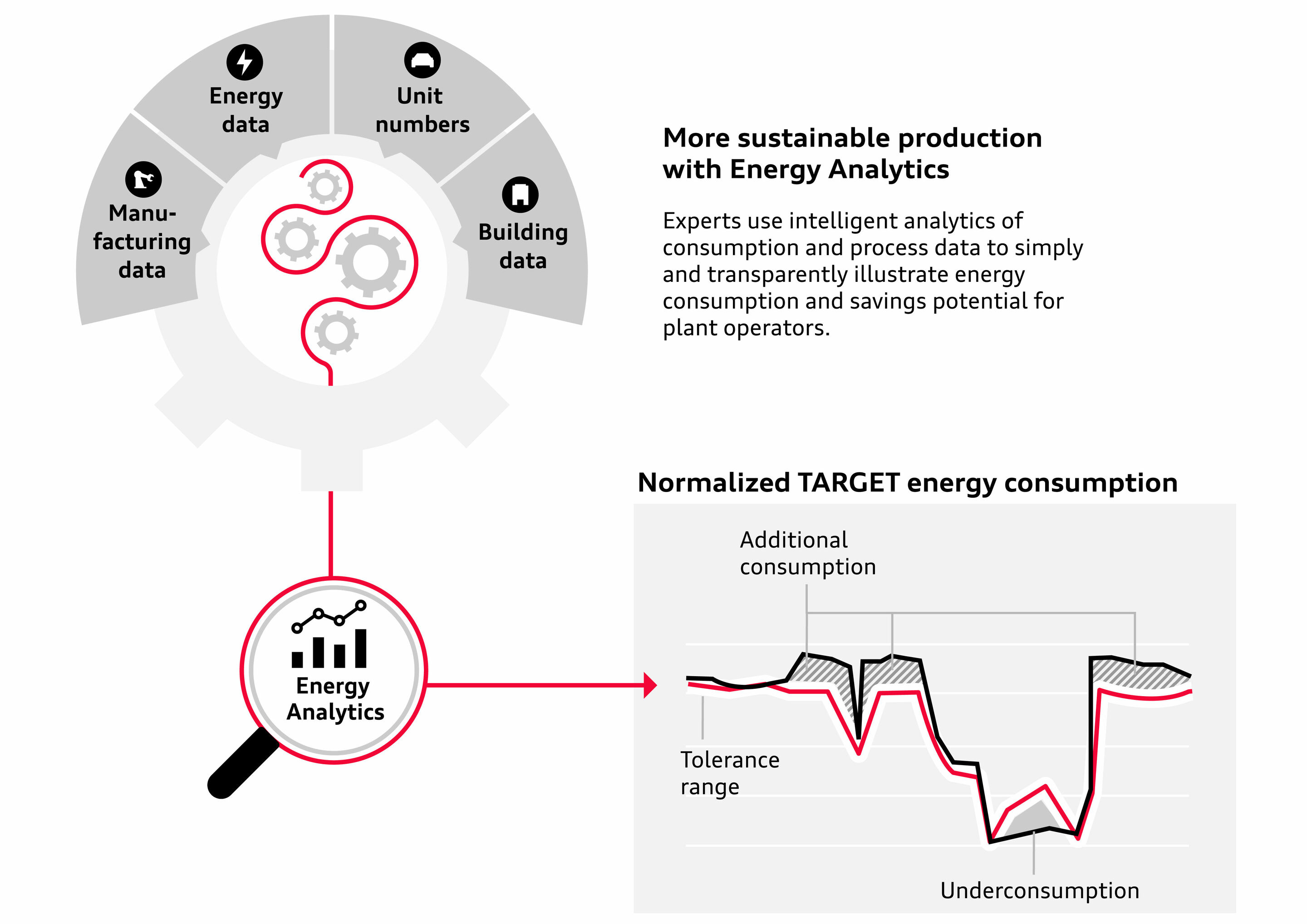
The platform Energy Analytics platform developed by Audi itself has made a significant contribution to achieving this goal. Energy Analytics is a software-based analysis system that performs live compilation, preparation, and processing of large quantities of data from production processes from various sources in the company. This process is known in general as data mining. The results are then depicted visually in such a way that users can quickly identify the key points of the analysis. This allows the causes of unnecessary energy consumption to be understood and categorized more easily, savings potential to be identified and ultimately suitable measures to be derived.
2. Producing renewable energy on site
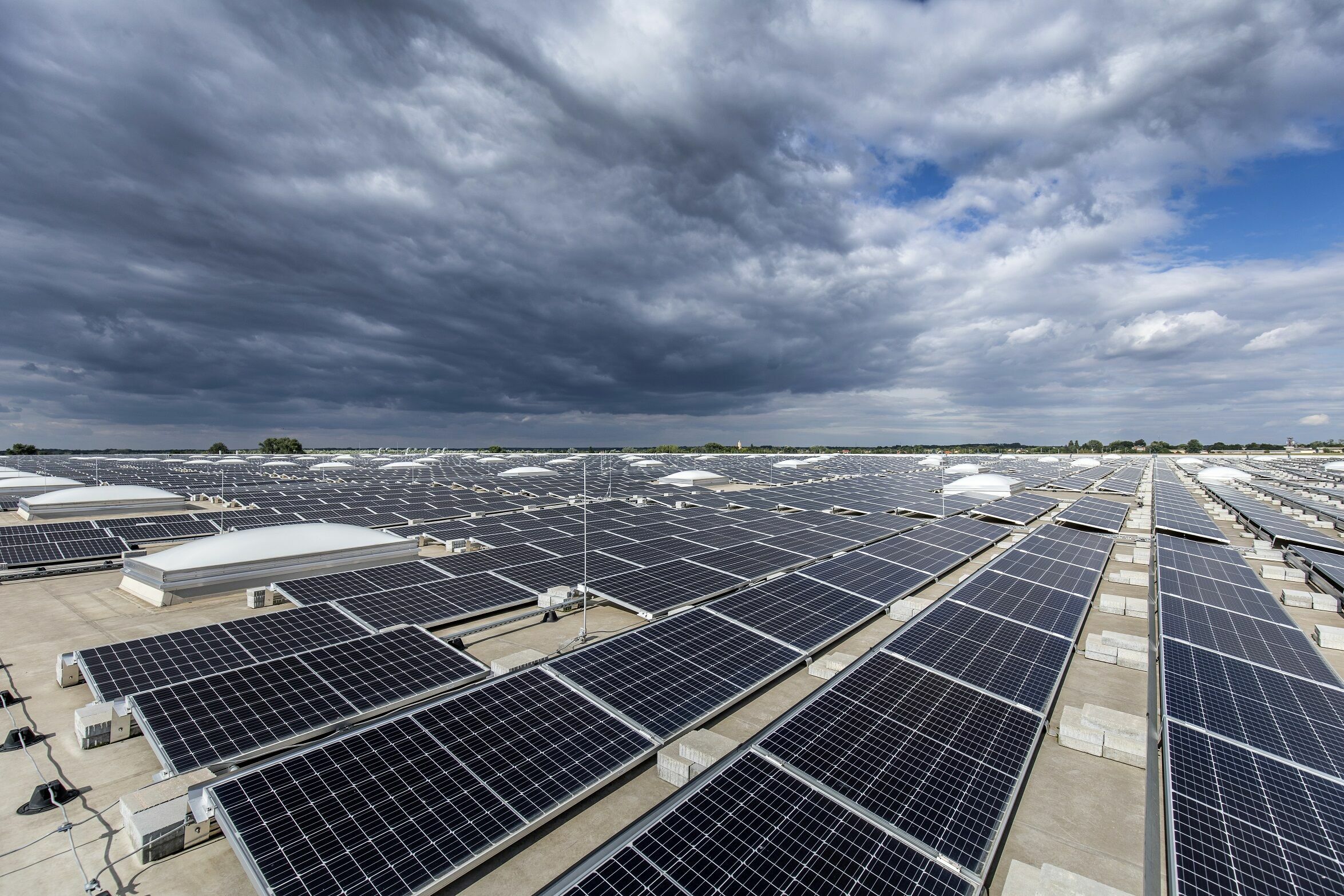
The second pillar of the concept: Audi also generates electricity from renewable sources in-house. To date, photovoltaic modules have been installed on an area of 23,000 square meters at the Ingolstadt plant. In the coming years, Audi will continue to increase the share of energy it generates itself at all its production sites. Around 41,000 square meters of photovoltaic modules are currently under construction or in planning at the main plant.
In addition to generating electricity, Audi is focusing on carbon-neutral1 in-house generation of thermal energy. And the company is planning to gradually increase this portion also, for example, through the use of heat pumps to reuse waste heat from production processes.
3. Purchasing renewable energy
As the third pillar of the concept, Audi is also transitioning its energy procurement to be net carbon neutral. Audi has been producing cars in Ingolstadt exclusively with green electricity since early 2012. This early transition made the brand with the four rings a pioneer of sustainability in the industry at the time.
Dr. Rüdiger Recknagel, Head of Environmental Protection for the Audi Group, explains: “A neighboring refinery and the municipal waste recycling plant supply the main plant with net carbon-neutral waste heat. Additionally, we have secured large quantities of biogas to ensure a net carbon-neutral heat supply.”
4. Offsetting carbon emissions that are currently unavoidable
In this way, the site covers almost all of its energy needs from renewable sources. As the fourth and final pillar, any emissions that Audi cannot yet avoid (a maximum of 10 percent of the original carbon emissions) are offset by purchasing carbon credits that are certified according to the highest quality standards such as Gold Standard. Only selected climate protection projects receive this independent quality standard. Through these certificates, Audi invests in the construction of wind turbines in the Global South, among other projects. In the case of the Ingolstadt plant, for example, the four Rings offset emissions from internal logistics.
Mission:Zero: Going beyond decarbonization
The measures of the environmental program Mission:Zero go beyond decarbonization and address the key areas of activity of water use, resource efficiency, and the protection and preservation of biodiversity. Audi’s vision is to create a circular economy where resources such as plastics, water, and other raw materials are used in closed cycles. In Ingolstadt, for example, the company has been operating a process water supply center with a membrane bioreactor since 2019 to use water more efficiently. This year, Audi became the first premium car manufacturer to join the Alliance for Water Stewardship (AWS). Audi plans to halve the ecologically weighted water consumption at its production sites worldwide by 2035. The plant in San José Chiapa, Mexico, which has been building cars without producing any wastewater since 2018, stands as a role model for the responsible use of water resources.
Finally, as a member of the “Biodiversity in Good Company” initiative, the brand with the four rings is also committed to protecting biodiversity at all its sites. The open spaces at the external site in Münchsmünster, which are designed to remain close to their natural form, are among the company’s largest measures in this area. On some 17 hectares of the site, a habitat has been created for numerous animal and plant species.
The 360factory and sustainable land use
Audi is also focusing on sustainability in the further development of its sites: Audi Production is using the transition to e-mobility to comprehensively transform its global production network and has a clear vision for the production of the future with the 360factory. As part of this holistic, sustainable approach, Audi is modernizing, digitalizing, and transforming its existing plants for the future. With the 360factory, Audi can achieve even greater flexibility and efficiency in production without sealing additional areas for new buildings.
When it comes to sustainable land use, Audi is going one step further by revitalizing a former industrial site. The incampus in the south of Ingolstadt is also integrated into the company’s sustainability activities as a branch of the main plant. A joint venture between AUDI AG and the city of Ingolstadt through its holding company IFG AöR, incampus GmbH has redeveloped a 75-hectare industrial wasteland in the east of Ingolstadt. A technology park was built there – without developing any new land. Fifteen hectares of the total area were designated as a compensation area for nature and landscape; a near-natural alluvial forest with nutrient-poor grassland now thrives there.
1Audi understands net-zero CO2 emissions to mean a situation in which, after other possible reduction measures have been exhausted, the company offsets the carbon emitted by Audi’s products or activities and/or the carbon emissions that currently cannot be avoided in the supply chain, manufacturing, and recycling of Audi vehicles through voluntary offsetting projects carried out worldwide. In this context, carbon emissions generated during a vehicle’s utilization stage, i.e. from the moment it is delivered to the customer, are not taken into account.