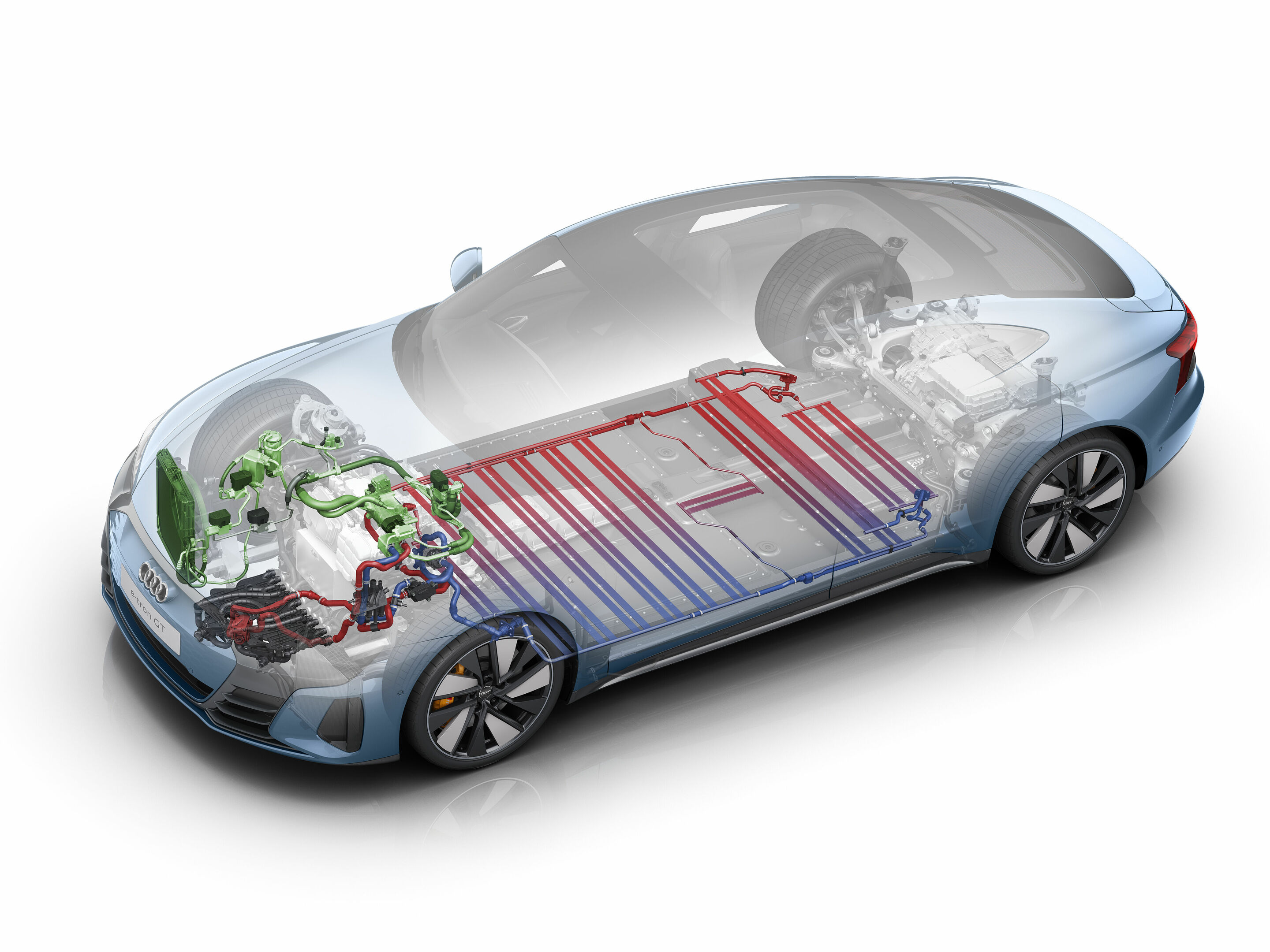
Battery and thermal management
Back to overviewThe lithium-ion battery system of the Audi e-tron GT quattro and the RS e-tron GT can store 84 kWh of energy net (93 kWh gross). It integrates 33 cell modules, each of which comprises 12 pouch cells with flexible outer skin. Each module is fitted with its own computer that monitors the temperature and voltage. The unusually high system voltage of approx. 800 volts enables a powerful continuous output and shortens the charging duration; in addition, it reduces the weight of, and space required by, the wiring.
The battery system is located beneath the passenger compartment, at the lowest point of the car. This, in combination with the electric motors, provides a low center of gravity appropriate for a sports car and a weight distribution between the front and rear axles that is very close to the ideal value of 50:50. Thirty modules form the lower level of the battery that features a wide recess in the rear section. It creates space for the rear passengers’ feet, which allows them to sit in a low position and also enables the flat vehicle silhouette. The upper “floor” contains three further modules situated below the rear seats. The connections, fuses, and the main control unit are located under the console of the center tunnel. The bottom of the battery is protected by an aluminium plate.
The inner structure of the battery that houses the module, the frame surrounding it, and the upper cover plate are made of aluminum. As in the body, die-cast sections, extruded sections, and aluminum sheets are used here. The battery system contributes significantly to the rigidity of the body to which it is attached via 28 screws. At the same time, it improves passive safety in the event of a frontal and side impact.
High-tech: thermal management
Beneath the cell space of the battery, there is a compound structure of flat extruded sections through which a glycol/water mixture flows that circulates in its own low-temperature circuit. The temperature is transferred between the cooling plates and the cell space via a heat-conducting paste. The battery’s feel-good temperature is between 30 and 35 degrees Celsius, and its operating range extends from minus 30 to plus 50 degrees.
Four separate coolant circuits, each at its own temperature level, regulate the temperature in the high-voltage components and the interior precisely and quickly. They can be interconnected flexibly as required. If the driver demands a high output several times in a row, valves couple the coolant circuit of the battery with the refrigerant circuit of the air-conditioning system – this intensive cooling keeps the performance of the drive at a consistently high level. The e-tron GT quattro and RS e-tron GT can accelerate to full speed from a standstill up to ten consecutive times.
The refrigerant circuit also helps with cooling during fast DC charging, which can heat the battery up to 50 degrees Celsius. The thermal management is connected to the navigation system. When the driver sets an HPC terminal (High Power Charging) as the destination, the cooling of the battery is already intensified on the way to the charging station so that it can be charged as quickly as possible. Should the battery still be very cold shortly after the car is started in winter, it is heated for fast charging.
The standard equipment of the e-tron GT includes a heat pump that heats the interior with the waste heat of the high-voltage components. It can reduce the loss of range that the electric climate control causes in winter in particular significantly. In addition to charging, customers can also manage pre-entry climate control of the interior via their smartphones using the myAudi app. This is done via a powerful high-voltage heating element and does not depend on the car charging via the power grid. Audi equips the e-tron GT with a deluxe auxiliary air-conditioning system as an option that also incorporates the steering wheel rim (if heatable), the exterior mirrors and the rear window.
From 11 to 270 kW: AC and DC charging
The charging flaps of the gran turismo are located behind the front wheels. Both sides feature connections for alternating current (AC) and there is also a connection for direct current (DC) on the right-hand side. The Audi e-tron GT is delivered to its customers with two charging cables as standard: one mode 3 cable for public AC terminals and the charging system compact for the garage. The e-tron GT can charge with 11 kW AC as standard, which allows it to recharge an empty battery overnight. An optional onboard charger for 22 kW will follow shortly after the market launch.
Audi offers the home charging system connect as an option. Its Internet connection enables both control via the myAudi app and function updates. In cooperation with a suitable home energy management system, it offers further intelligent functions. For example, the e-tron GT can take account of the needs of other consumers in the household, and charge with the remaining power available in order to avoid overloading. Customers can also define individual priorities, such as charging when electricity is less expensive under a variable electricity rate.
At a direct current terminal with a voltage of 800 V, for example in the European freeway network from Ionity, the Audi e-tron GT achieves a peak charging capacity of up to 270 kW. This allows it to recharge energy for up to 100 kilometers (62.1 mi) in just over five minutes, and charging from five to 80 percent SoC (state of charge) takes less than 22.5 minutes under ideal conditions. The driver can restrict the charging target in the MMI operating system, for example if the rate appears too high.
Customers in Europe can use the Audi brand’s own e-tron Charging Service, which currently incorporates roughly 200,000 public charging points. A special card is needed to access them, and Audi customers pay a standard rate across 26 countries. Ionity’s fast-charging network offers customers a range of favorable terms and conditions. In the first year, Audi covers the basic fee for the transit rate, which offers a reduced price for electricity.
In the NEDC cycle, the Audi e-tron GT quattro consumes 19.6–18.8 kWh of energy per 100 kilometers (62.1 mi) on average, the RS model consumes 20.2–19.3 kWh. This results in average ranges of up to 488 kilometers (303.2 mi) or 472 kilometers (293.3 mi) (WLTP).
All terms marked in the text are explained in detail in the technology lexicon at www.audi-mediacenter.com/en/technology-lexicon. The equipment, data and prices specified in this document refer to the model range offered in Germany. Subject to change without notice; errors and omissions excepted.